Key Features of TOPs Cells
Minimally invasive
 Cells can be obtained in a sufficient quantity for treatment from approximately 0.2 g of adipose tissue equivalent to approximately 4-5 grains of rice, collected using a biopsy needle.
Cells can be obtained in a sufficient quantity for treatment from approximately 0.2 g of adipose tissue equivalent to approximately 4-5 grains of rice, collected using a biopsy needle.
Adipose tissue collection using a biopsy needle offers the following advantages:
・Minimally invasive to the body
・Low risk of scar formation (no need for sutures or stitch removal)
・Can be performed even in lean individuals
・Short procedure time (approximately 20 minutes)
Development of the Biopsy Needle
Biopsy Needle
Adipose tissue can be collected more reliably and consistently using a biopsy needle jointly developed by CPC corp. and Toray Medical Co., Ltd.
-
Unique Tip Design (Proprietary Shape)
Ablunt, non-cut tip reduces the risk of internal bleeding by eliminating sharp edges. -
Simple Structure
This intuitive and easy-to-use design allows smooth operation even for first-time users. The spring-loaded mechanism enables stable collection of adipose tissue. -
High Cell Outgrowth Efficiency
Compared to fat tissue collection using a scalpel or scissors, this method offers superior efficiency in cell culture and derivation.

Non-enzymatic processing
 cells are obtained with minimal damage to the cells.
cells are obtained with minimal damage to the cells.
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are widely accepted and can be cultured after collagenase treatment of the adipose tissue. However, several challenges have been encountered.
- The procedure is complex and requires multiple steps.
- Since collagenase breaks down the extracellular matrix, excessive treatment may damage the cells.
- Collagenase is primarily extracted from bacteria, and its activity can vary, making it difficult to standardize the treatment time and concentration.
- Concerns also include high costs and potential immune responses.
Development of a Culture Substrate for Enzyme-Free Primary Culture
In enzyme-free processing using a culture substrate, adipose tissue adheres to the substrate, and cells are isolated by utilizing their natural outgrowth. Therefore, a culture substrate that firmly retains adipose tissue and facilitates efficient cell outgrowth is required.
We collaborated with an academic research institution and Japan Vilene Company, Ltd. to develop a specialized nonwoven fabric as a cellular scaffold to address this (Japanese Patent Application No. 2022-190774).
The method of isolating stem cells using this nonwoven fabric has been shown to yield a significantly higher number of cells per milligram of adipose tissue than enzymatic digestion.
Furthermore, no abnormalities were observed in cell proliferative capacity, differentiation potential, or surface marker expression(Regen Ther. 2022 Jun 8:21:52-61).
This technology enables the primary culture of TOPs cells from a small amount of adipose tissue without the need for enzymatic treatment.

| Effect of Enzymatic Treatment During Primary Culture | None |
|---|---|
| Required Amount of Adipose Tissue | Small |
| Culture Cost | Low |
Consistent Quality
We provide standardized, quality-assured cells to all patients.
-
Need for Personalized Culturing
Because the characteristics of tissues and cells vary from patient to patient, it is necessary to adjust culture conditions to meet quality standards. Based on the accumulated culture data, we designed optimal culture processes tailored to individual needs.
-
Ensuring Sufficient Cell Yields
The proliferative capacity of autologous cells differs among individuals, making it challenging to consistently obtain the number of cells required for treatment. We developed a specialized culture medium optimized for cell growth to ensure that a sufficient number of cells can be obtained from any patient to address this issue.
-
Reducing the Volume of Autologous Serum Required
We used a culture medium that enables stable cell growth with only a small amount of autologous serum to minimize the burden of blood collection on patients. This enabled us to secure the necessary number of cells for treatment while reducing the burden on patients.
Development of a Specialized Culture Medium for More Stable Cell Culturing
- Through joint research with an academic research institution and Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., we developed a specialized culture medium called "ciKIC MSC Medium TOPs II" (hereafter referred to as TOPs Medium II). This animal-free medium was designed for mesenchymal stem cells and demonstrated strong proliferative support even under low-serum conditions. This enables cell culture with full traceability and control of the raw materials used in the medium.
- ciKIC® MSC Medium TOPs® II — Culture Medium for Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Features of Medium II
Medium II
・Animal-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
・Excellent support for cell proliferation
・Certified for suitability as raw material for regenerative medical products
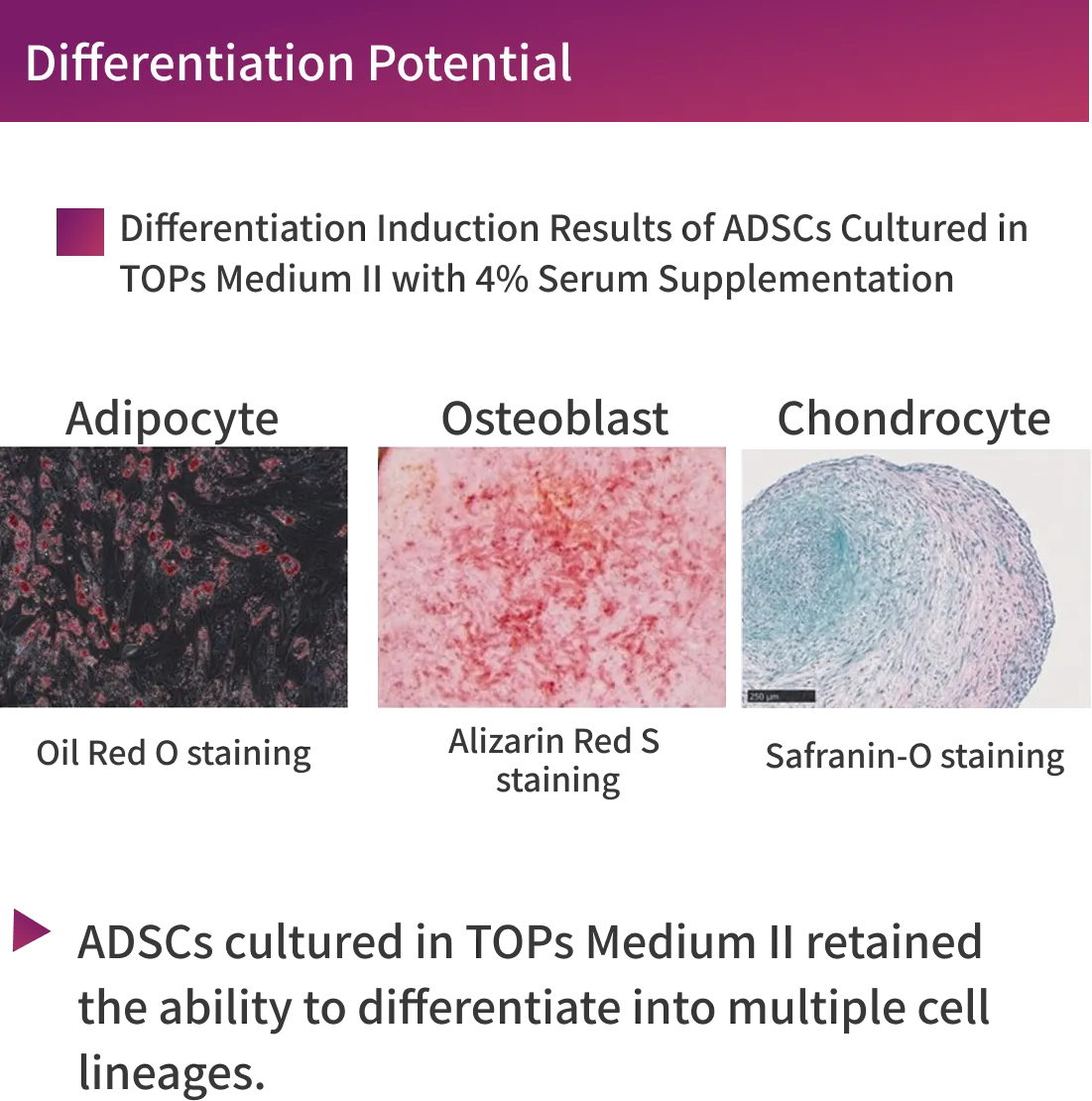
・Consistent differentiation potential
・Low-serum formulation

(Source : Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., https://www.kanto.co.jp/dcms_media/other/BBz-37.pdf )
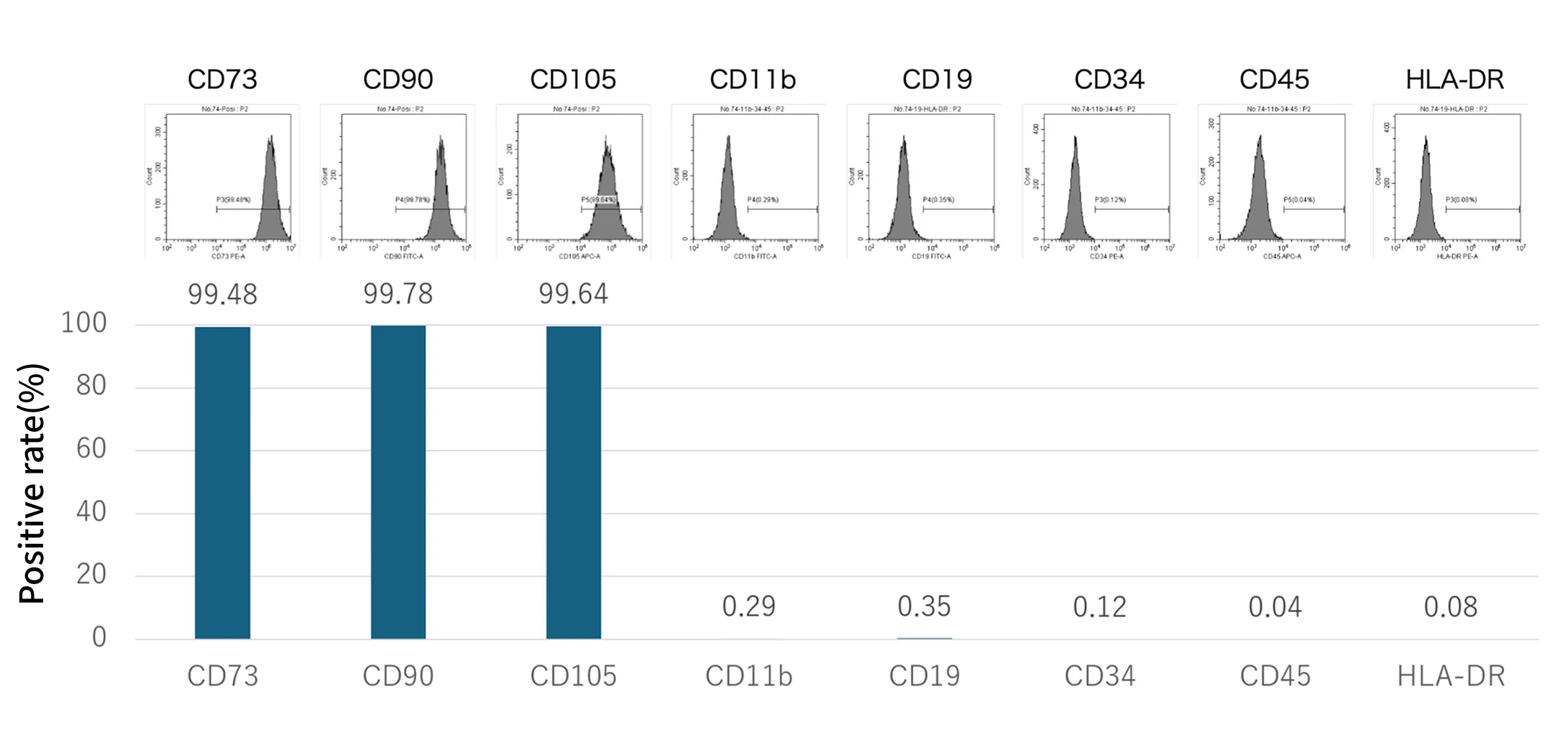
Periodic Evaluation of Cell Surface Marker Expression
TOPs cells meet the criteria for Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as defined by the International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy (ISCT). (Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-7. )
Non-frozen
In regenerative medicine, cells used immediately before treatment can be either frozen or non-frozen. Even among the regenerative medical products approved under the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, some are thawed at the bedside, whereas others are provided in a non-frozen state.
Each approach has advantages and disadvantages.
In general, cultured cells are often evaluated without freezing, and much of the research data we obtained is based on cells in a non-frozen state.
Valuing the accumulated research data and ensuring that physicians can confidently provide cells to patients, TOPs cells can be supplied as safe, non-frozen cells by strictly controlling the temperature during transportation.
(Treatment schedule adjustments are managed through intermediate freezing.)
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-frozen |
|
|
| Frozen |
|
|
-
Stem cell therapy
-
What are Stem Cells?
-
Regenerative therapies with stem cells
-
-
Cells
-
Implementing Facility


